Heat Load Calculation - Terminology:
Objective of the Heat load calculation :
* Equipment Selection.
*Optimize the load value.
* System Design ,Operation & control.
Terminologies used in Heat load Calculation:(Ashrae Standard 12-75, Refrigeration Terms and Definitions.)
1) Space.
2) Room.
3) Zone.
4) British Thermal unit.
5) Cooling load Thermal Difference.
6) Sensible Heat Gain.
7) Latent heat Gain.
8) Radiant Heat Gain.
9) Space Heat Gain.
10) Space Cooling Load.
11) Space Heat Extraction rate.
12) Dry Bulb Temperature.
13) Wet bulb Temperature.
14) Dewpoint Temperature.
15) Relative Humidity.
16) Heat Transfer co-efficient.
17) Thermal Resistance(R).
Space :
It is either a volume or a site without a partition or a partitioned room or group of rooms.
Room :
It is an enclosed or partitioned space that is usually treated as single load.
Zone :
it is a space or group of spaces within a building with heating and/or cooling requirements sufficiently similar so that comfort conditions can be maintained throughout by a single controlling device.
British thermal unit (Btu) :
It is the approximate heat required to raise 1 lb. of water 1 deg Fahrenheit, from 59 deg F to 60 deg F.
• 1 ton is equivalent to 12,000 BTU/hr. and
• 12,000 BTU/hr is equivalent to 3,516 Watts - or 3.516 kW (kilo-Watts).
Cooling Load Temperature Difference (CLTD) :
It is an equivalent temperature difference used for calculating the instantaneous external cooling load across a wall or roof.
Sensible Heat Gain :
It is the energy added to the space by conduction, convection and/or radiation.
Latent Heat Gain :
It is the energy added to the space when moisture is added to the space by means of vapor emitted by the occupants, generated by a process or through air infiltration from outside or adjacent areas.
Radiant Heat Gain :
It is the rate at which heat absorbed is by the surfaces enclosing the space and the objects within the space.
Space Heat Gain :
It is the rate at which heat enters into and/or is generated within the conditioned space during a given time interval.
Space Cooling Load :
It is the rate at which energy must be removed from a space to maintain a constant space air temperature.
Space Heat Extraction Rate :
It is the rate at which heat is removed from the conditioned space and is equal to the space cooling load if the room temperature remains constant.
Dry Bulb Temperature :
It is the temperature of air indicated by a regular thermometer.
Wet Bulb Temperature :
It is the temperature measured by a thermometer that has a bulb wrapped in wet cloth. The evaporation of water from the thermometer has a cooling effect, so the temperature indicated by the wet bulb thermometer is less than the temperature indicated by a dry-bulb (normal, unmodified) thermometer.
Dewpoint Temperature :
It is the temperature to which air must be cooled in order to reach saturation or at which the condensation of water vapor in a space begins for a given state of humidity and pressure.
Relative humidity :
It describes how far the air is from saturation. It is a useful term for expressing the amount of water vapor when discussing the amount and rate of evaporation. One way to approach saturation, a relative humidity of 100%, is to cool the air. It is therefore useful to know how much the air needs to be cooled to reach saturation.
Thermal Transmittance or Heat Transfer Coefficient (U-factor) :
It is the rate of heat flow through a unit area of building envelope material or assembly, including its boundary films, per unit of temperature difference between the inside and outside air. The U-factor is expressed in Btu/ (hr deg F ft2).
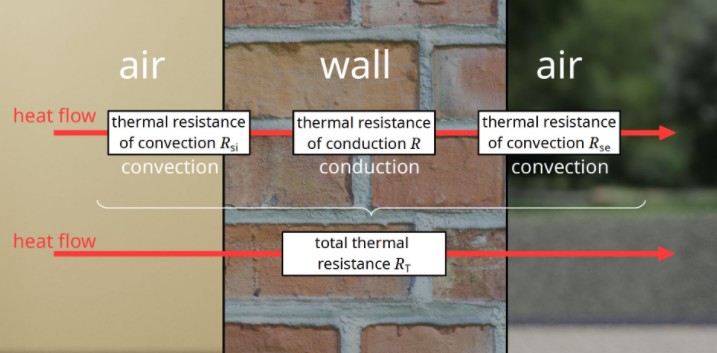
Thermal Resistance (R) :
It is the reciprocal of a heat transfer coefficient and is expressed in (hr degree F ft2)/Btu. For example, a wall with a U-value of 0.25 would have a resistance value of R = I/U = 1/0.25=4.0. The value of R is also used to represent Thermal Resistivity, the reciprocal of the thermal conductivity.









0 Comments